![How Common Is Erectile Dysfunction [Statistics]](https://wp.bedbible.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Erectile-Dysfunction-Statistics.png)
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is more than just a medical condition; it’s a topic that touches on the core of masculinity, relationships, and self-worth. As a condition that affects a man’s ability to achieve or maintain an erection, ED can have profound implications on mental well-being, relationships, and overall quality of life.
This comprehensive statistical piece aims to provide an in-depth understanding of ED.
Here’s what you can find in this report:
- Prevalence of ED
- Age and ED
- Causes and Risk Factors
- ED and Comorbidities
- Treatment and Management
- Economic and Societal Impact
- Data and Methodology
Key Findings
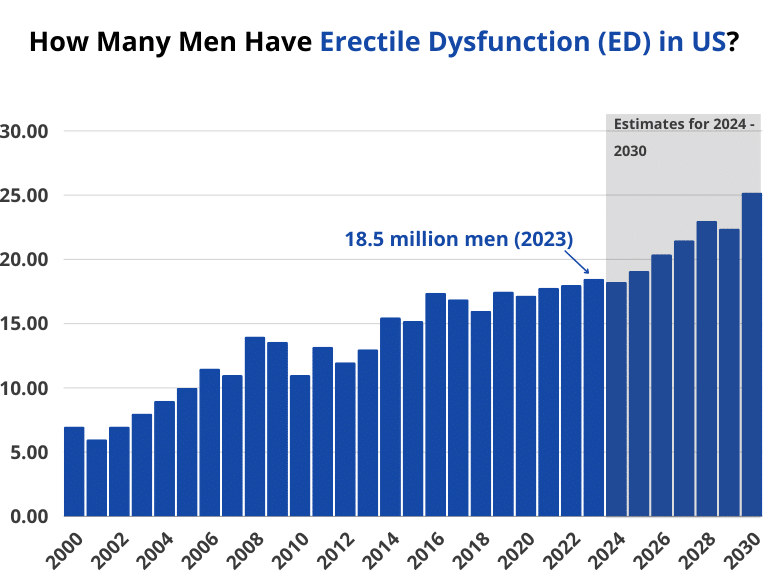
- In the US 18.5 million men suffer from ED. That’s nearly 1 out of 5 men. (322 million globally).
- The US is the country with the highest number of EDs (25%), and Spain with the lowest (10%)
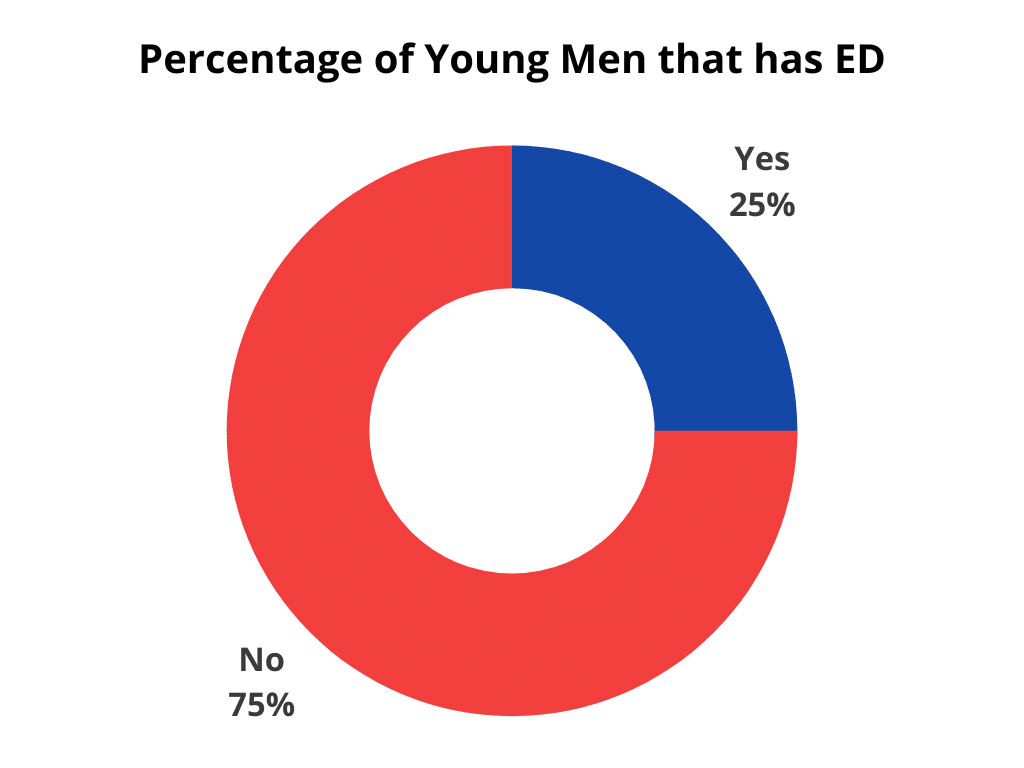
- About 25% of men under 40 years experience ED
- By age 70, nearly 70% of men experience some form of ED
- Only 25% of men suffering from ED pursue and receive treatment
- Patients with ED spend approximately $120 annually on treatment
- 75% of men say Viagra helped them.
- 8 out of 10 men with ED are overweight (BMI above or equal to 25).
- ED patients get more heart attacks than people who don’t.
Prevalence of ED
- Global Prevalence: An estimated 322 million men worldwide will be affected by ED by 2025. This number underscores the global scale of the issue.
- US Statistics: Approximately 18.5 million men in the US suffer from ED. This means that nearly one in five men in the US faces challenges related to ED.
- 1 in 10 men has tried to have ED.
- The US is the country with the highest number of EDs (25%), and Spain with the lowest (10%).
Age and ED
- Young Men: About 25% of men under 40 years experience ED. This challenges the misconception that ED is solely an older man’s issue.
- Middle-Aged Men: The prevalence of ED increases to about 40% by age 40, indicating that middle age is a critical period for ED onset.
- Senior Men: By age 70, nearly 70% of men experience some form of ED, emphasizing the strong correlation between age and ED.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Physical Causes: Conditions like heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity are leading physical causes. These conditions can impair blood flow, a critical component for achieving an erection.
- Psychological Causes: Stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship issues can lead to ED. The mind plays a pivotal role in sexual arousal, and psychological disturbances can disrupt this process.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use can exacerbate ED symptoms. These factors can impair blood flow and disrupt hormonal balance.
- 42% of men who have diabetes will also experience Erectile Dysfunction.
- 8 out of 10 men with ED are overweight (BMI above or equal to 25).
- ED patients experience more heart attacks than people who don’t.
- An ED also increases the probability of experiencing depression (210%).
ED and Comorbidities
- Cardiovascular Disease: ED can be an early warning sign of cardiovascular issues. The blood vessels in the penis are narrower than those in the heart, making them more susceptible to blockages.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, impairing the body’s ability to respond to sexual stimuli.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can damage blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the penis.
Treatment and Management
- Pharmacological Treatments: These are the most commonly prescribed medications for ED. Examples include Viagra (sildenafil), Cialis (tadalafil), and Levitra (vardenafil). They work by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating an erection in response to sexual stimulation.
- Testosterone Replacement: For men with low testosterone levels, testosterone replacement therapy can be an effective treatment.
- Non-Pharmacological Treatments: Vacuum Erection Devices (penis pumps) are external pumps with a band that can be used to attain and maintain an erection. Penile Implants are devices surgically implanted into the penis and can be inflatable or malleable.
- Lifestyle Changes: A balanced diet and regular exercise can improve cardiovascular health, which in turn can reduce ED symptoms. Reducing alcohol and quitting smoking can significantly improve erectile function.
- Psychological Counseling: For many men, ED has a psychological component. Therapy can address issues like anxiety, depression, and relationship challenges, which can contribute to ED.
- Alternative Treatments: Some men find relief from ED through acupuncture, though scientific evidence on its efficacy is mixed. Herbal remedies, like ginseng, are believed to treat ED, but it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any herbal remedies.
- Emerging Treatments: Stem Cell Therapy involves injecting stem cells into the penis to repair damaged tissue and blood vessels. Shockwave Therapy is a non-invasive procedure that uses low-intensity shock waves to improve blood flow to the penis.
- 75% of men say Viagra helped them.
Economic and Societal Impact
- Cost Implications: The global market for ED drugs is vast, with billions spent annually. This underscores the demand for effective treatments.
- Societal Implications: Beyond the individual, ED affects relationships and families. The strain on relationships can lead to broader societal challenges, including mental health issues and relationship breakdowns.
- Only 25% of men suffering from ED pursue and receive treatment.
- Among those seeking treatment for ED, 25% are under the age of 40.
- The global expenditure on the top three ED medications, namely Viagra, Levitra, and Cialis, exceeds $1 billion annually.
- PDE5 inhibitors, which include popular ED pills, account for just 37% of the total yearly expenses related to ED. The remaining costs are associated with medical consultations, diagnostic tests, hormone therapies, and other related services.
- On average, patients with ED spent approximately $120 annually on treatment, such as Viagra, back in 2001.
- In cases where ED medications are ineffective, penile prosthesis surgery emerges as a long-term, cost-effective solution. Despite potential costs reaching $20,000, many insurance plans, including Medicare, typically cover penile implant procedures.
Data and Methodology
In our pursuit to provide the most accurate and comprehensive insights on Erectile Dysfunction (ED), we have employed a rigorous data collection and analysis methodology. Our approach is rooted in the principles of scientific research, ensuring that the information we present is both trustworthy and authoritative.
1. Source Selection
We prioritized data from reputable medical journals, health organizations, and established research studies. By focusing on these trusted sources, we ensured that our information was based on credible, peer-reviewed research.
2. Data Collection
Our team of researchers meticulously reviewed each source, extracting relevant statistics, insights, and trends related to ED. This hands-on approach allowed us to gather a diverse range of data, ensuring a holistic understanding of the topic.
3. Data Validation
To maintain the integrity of our findings, we cross-referenced data points across multiple sources. This validation process helped identify and rectify any discrepancies, ensuring the accuracy of the information we presented.
4. Analysis
Beyond just presenting raw data, we delved deep into the numbers to identify patterns, correlations, and underlying causes. Our analytical approach provides readers with a nuanced understanding of ED, its prevalence, causes, and implications.
5. Peer Review
Before finalizing our findings, our research was subjected to an internal peer review. This added layer of scrutiny ensured that our conclusions were sound, logical, and free from bias.
6. Continuous Updates
Recognizing that medical research is an ever-evolving field, we commit to regularly updating this piece with the latest findings and statistics. This ensures that our readers always have access to the most current information on ED.
