![How Common Is Incest [Statistics & Facts]](https://wp.bedbible.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/how-common-is-incest-in-the-us.png)
Across 292 different published and peer-reviewed articles we have gathered meta-data on incest.
Collectively the dataset includes data points from more than 11,311,428 participants and survey respondents.
The historical data spans from 1980 to 2023. This makes it the most comprehensive meta-study of incest ever assembled and published.
Here’s what you’ll find in this article:
- Prevalence of incest
- Types of incest
- Demographics
- What happens during incest
- What happens after – the consequences
- Laws against incest
- Consensual incest on the rise?
- History and religion
Key Statistics
- 15% of US families have had incest events in the family.
- 32 million Americans report to have been the victims of incest as a child (12.7% of all adults in the US).
- 1 in 5 girls have been victims of incest (compared to 1 in 14 boys).
- 20% of incest victims report the crime to law enforcement.
- 46% of all children under 18 who are raped, have been raped by someone in their own family.
- 74.4% of incest cases happen within the biological family.
- 25.6% of incest cases with someone related, e.g. step-father (without consanguinity)
- The most frequent type of incest is father-daughter incest (34.8% of all incest cases is father-daughter; 23.1% is brother-sister; 6.1% is mother-son).
- 15% of the females and 10% of the males reported some type of sexual experience involving a sibling.
- 70.8% of all who experienced incest were under 18 when it happened the first time (29.2% were 11 or younger, and 43.3% were 12 or younger).
- Over 50% of pornvideos on pornhub have an incestuous angle (title, video theme, or �‘characters played’).

Prevalence of incest
- It is estimated that 10-15% of US families have had incest happen in their family.
- More than 32 million Americans report that they have had a parent rape them as a child.
- 12.7% of all adults self-report to have experienced sexual abuse from a family member as a child.
- Only 20% of victims of incest report the crime committed against them.
- 43-46% of children who are raped are raped by members of their own family.
- 90% of sexual abuse against children under 18 is perpetrated by members of the victims family.
Types of incest
There are many different types of incest, and in the following sections we discuss some of these types, the prevalence of them. Lastly, we compare the prevalence of them compared to each other.
- 74.4% of all cases of incest happen between biological family members (blood-related).
- 25.6% of all cases of incest happen between adopted or step-family members (non-blood related).
Father and daughter incest
- 34.8% of all incestuous encounters happen between a daughter and her biological father.
- Father-daughter incest (biological) is the most common type of incest.
Step-father and step-daughter incest
- 12% of all incestuous encounters happen between a step-daughter and step-father.
- Step-fathers are 8 times as likely as biological fathers to sexually assault a step-daughter while living together.
Brother and sister incest
- 23.1% of incest cases happen between a brother and a sister.
- 81% of brother-sister incest cases are between and older brother and younger sister.
Mother and son incest
- 25.4% of male incest victims reported it as mother-son incest.
- 6.1% of incest events were between a mother and son (with and without consanguinity).
Demographics
- 55% of adult incest perpetrators were unemployed
- in 79.1% of the families where incest occurred had 3 or more children.
- 30.2% of individuals who self-reported to have had an incestual sexual encounter were over 18.
- 83.7% of incest victims are female.
- 16.3% of incest victims are male.
- Parents that engage in frequent verbal or physical fighting are 5 times more at risk as a family of father-daughter incest.
- 18.7% of girls are victims of some form of incest.
- 7.2% of boys are victims of some form of incest.
Age of victims
- 70.8% of incest victims were 18 or under when it happened.
- 29.2% of incest victims were under 11 years old when it happened.
| Age | % of all victims (age of first incest event) | %, Summative |
|---|---|---|
| 0-2 | N/A (not reliable data due to non-reports) | – |
| 3 | 0.1% | 0.1% |
| 4 | 1.2% | 1.3% |
| 5 | 0.8% | 2.1% |
| 6 | 1.7% | 3.8% |
| 7 | 3.3% | 7.1% |
| 8 | 2.3% | 9.4% |
| 9 | 4.1% | 13.5% |
| 10 | 7.9% | 21.4% |
| 11 | 7.8% | 29.2% |
| 12 | 14.1% | 43.3% |
| 13 | 11.2% | 54.5% |
| 14 | 7.1% | 61.6% |
| 15 | 3.1% | 64.7% |
| 16 | 1.2% | 65.9% |
| 17 | 2.8% | 68.7% |
| 18 | 2.1% | 70.8% |
| >18 | 29.2% | 100.0% |
What happens during incest
- In 54.5% of incest cases, respondents report that penetration was a part of the sexual encounter.
- 33% of incest victims experienced anal penetration
- 32.6% of incest events last for more than one year.
- 93.1% of incest victims were not physically assaulted.
What happens after – the consequences
- 93% of women who experience abuse from their fathers develop an eating disorder at some point in life.
- All of the women who report having been abused by their fathers during childhood have been diagnosed with depression.
- 55-65% of sexual offenders have been the victims of incest during childhood.
- Sexual abuse victims are 11 times more likely to become Incestual offenders compared to people who have not.
- Incest victims have on average 16% higher health costs (doctors, psychiatrists, medicine, etc.).
- Incestual relationships can lead to inbreeding which can cause congenital disorders, disabilities (mental and physical), and developmental issues for the children.
Laws against incest
- Most Western countries have banned incest based on reasoning around inbreeding.
- However, most countries do not categorize first-, or second-cousin relationships for incest.
- 8-11% of relationships in South America, East Asia, and Southern Europe are between first-, or second-cousins.
- 50% of all relationships in the Middle East, North Africa, and South Asia are between first-, or second cousins.
US laws
In the us, laws are on a state-by-state basis:
| State | Prison sentence | Fine |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 1 to 10 years | $15,000 |
| Alaska | 2 to 12 years | $50,000 |
| Arizona | 1 to 3.75 years | N/A |
| Arkansas | 3 to 10 years | $10,000 |
| California | max 3 years | $10,000 |
| Colorado | 2 to 12 years | up to $750,000 |
| Connecticut | 1 to 5 years | $5,000 |
| Delaware | max 1 year | $2,300 |
| Florida | max 15 years | $5,000 |
| Georgia | 10 to 30 years | N/A |
| Hawaii | max 5 years | N/A |
| Idaho | maximum life sentence | N/A |
| Illinois | 2 to 10 years | $25,000 |
| Indiana | 1 to 6 years | N/A |
| Iowa | max 5 years | $7,500 |
| Kansas | 5 months to 11.3 years | N/A |
| Kentucky | 5 years to life | N/A |
| Louisiana | 5 to 30 years | N/A |
| Maine | max 5 years | $5,000 |
| Maryland | 1 to 10 years | N/A |
| Massachusetts | max 20 years | N/A |
| Michigan | max 2 years | $500 |
| Minnesota | max 10 years | N/A |
| Mississippi | max 10 years | $500 |
| Missouri | max 7 years | N/A |
| Montana | maximum life sentence | N/A |
| Nebraska | 1 to 25 years | N/A |
| Nevada | 2 years to life | $10,000 |
| New Hampshire | 10 to 20 years | N/A |
| New Jersey | 18 months to 15 years | N/A |
| New Mexico | max 3 years | $5,000 |
| New York | 10 to 25 years | N/A |
| North Carolina | 10 months to 15.2 years | N/A |
| North Dakota | max 5 years | $10,000 |
| Ohio | 2 to 6 years | N/A |
| Oklahoma | max 10 years | N/A |
| Oregon | max 20 years | $375,000 |
| Pennsylvania | max 10 years | N/A |
| Rhode Island | No criminal prosecution for 16+ | N/A |
| South Carolina | 6 months to 5 years | minimum $500 |
| South Dakota | max 15 years | $30,000 |
| Tennessee | 3 to 15 years | $10,000 |
| Texas | 2 to 20 years | $10,000 |
| Utah | max 5 years | $5,000 |
| Vermont | max 5 years | $1,000 |
| Virginia | 1 to 20 years | up to $100,000 |
| Washington | max 10 years | up to $10,000 |
| West Virginia | 5 to 15 years | $500 to $5,000 |
| Wisconsin | max 40 years | $100,000 |
| Wyoming | max 15 years | $10,000 |
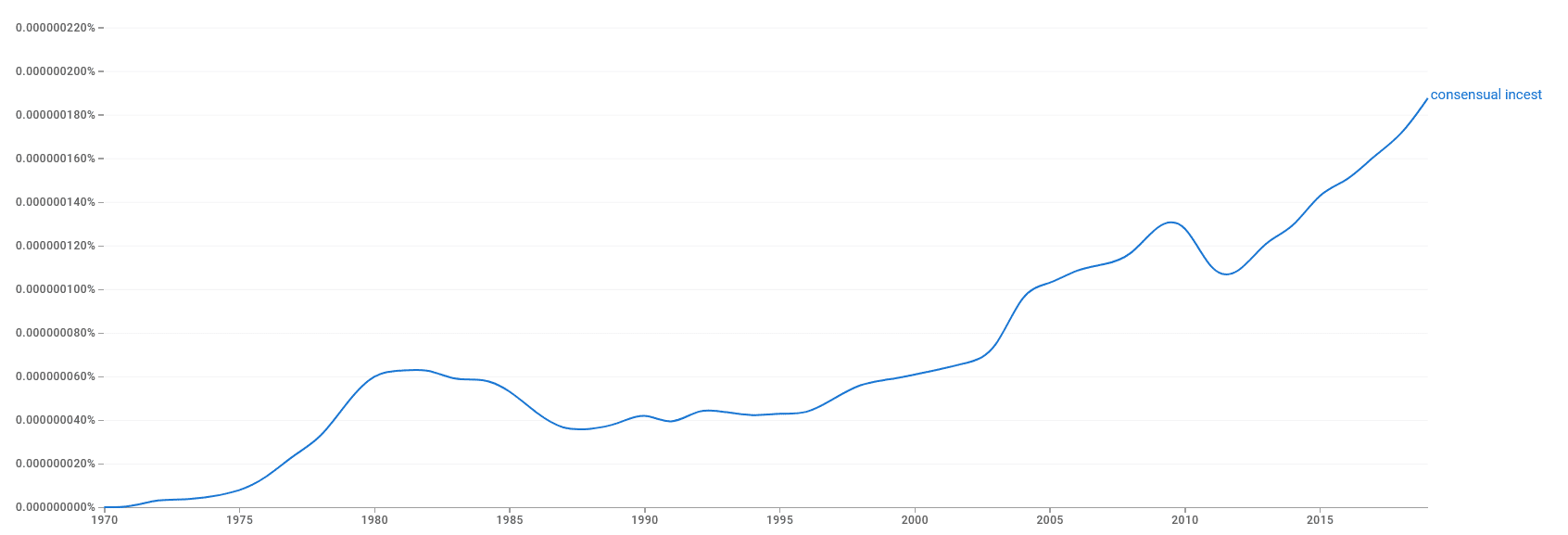
Consensual incest on the rise?
Looking at data on “consensual incest” we found an interesting pattern, that it since 1970 has gained more than x190 times the interest. The question then becomes if it is more prevalent than earlier or simply more talked about.
A single study found that 30% reported positive reactions to incest between siblings. However, multiple studies have shown that a lot of victims of incest suffer from distorted and disturbed views about their own experiences.
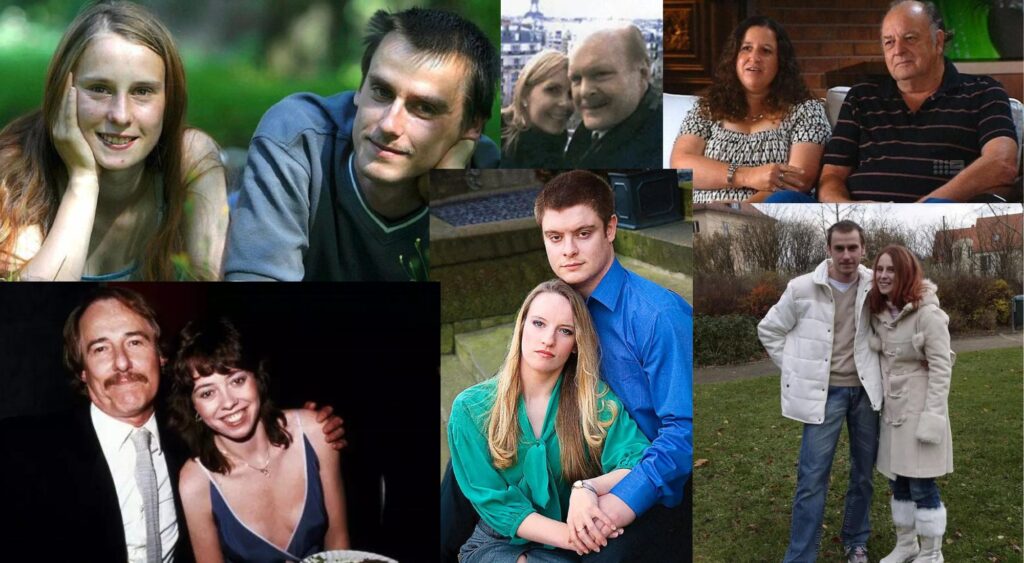
That being said, there have been a lot of media stories about sibling couples. Some include:
- Bruce McMahan and Linda McMahan – a UK couple, Father-daughter incest, married in 2004, have since separated.
- John Deaves and Jenny Deaves – Australian couple, father-daughter incest, interviewed by 60 minutes, arrested after a child suffered a heart defect and died.
- Danielle Heaney and Nick Cameron – half-brother-sister incest, met when they were 20 and 26 years old, from Scotland, sentenced to 9-month probation, living together.
- Patrick Stuebing And Susan Karolewski – step-brother-sister incest, German couple, Stuebing was adopted at birth and raised in the family, work as activists to change German laws on incest.
- Mackenzie Phillips and John Phillips – father-daughter incest, John Phillips was a part of the band “The Mamas and the Papas”, moved to Mexico and raised Mackenzie’s younger siblings as their own.
- Allen Muth and Patricia Muth – brother-sister incest, from Wisconsin, the couple met as adults and had children together, eventually they faced 5 and 8 years in prison each.

Prevalence in porn
- Over 50% of the porn on Pornhub featured some form of incest
- The share of incest videos increases on average by 1.5% each year (since 2016).
History and religion
We are not as concerned with these aspects – both the historical aspect of the first story e.g. mother-son incest from the roman Oedipus story. Nor the specific religious attitudes towards incest.
Sources
- Adams, M. S., & Neel, J. V. (1967). Children of incest. Pediatrics, 40(1), 55-62.
- Adler, N. A., & Schutz, J. (1995). Sibling incest offenders. Child Abuse & Neglect, 19(7), 811-819.
- Alexander, P. C. (1985). A systems theory conceptualization of incest. Family process, 24(1), 79-88.
- Archibald, E. (2001). Incest and the medieval imagination. OUP Oxford.
- Bagley, C. (1969). Incest behavior and incest taboo. Social Problems, 16(4), 505-519.
- Baird, P. A., & McGillivray, B. (1982). Children of incest. The Journal of Pediatrics, 101(5), 854-857.
- Ballantine, M. W. (2012). Sibling incest dynamics: Therapeutic themes and clinical challenges. Clinical Social Work Journal, 40, 56-65.
- Banning, A. (1989). Mother-son incest: Confronting a prejudice. Child Abuse & Neglect, 13(4), 563-570.
- Becker, J. V., Kaplan, M. S., Cunningham-Rathner, J., & Kavoussi, R. (1986). Characteristics of adolescent incest sexual perpetrators: Preliminary findings. Journal of Family Violence, 1, 85-97.
- Bell, V. (2002). Interrogating incest: Feminism, Foucault and the law. Routledge.
- Bessa, M. M. M., Drezett, J., Adami, F., Araújo, S. D. T. D., Bezerra, I. M. P., & Abreu, L. C. D. (2019). Characterization of adolescent pregnancy and legal abortion in situations involving incest or sexual violence by an unknown aggressor. Medicina, 55(8), 474.
- Bienen, L. B. (1997). Defining incest. Nw. UL Rev., 92, 1501.
- Blume, E. S., & Lawrence, J. (1990). Secret survivors: Uncovering incest and its aftereffects in women (p. 352). New York: Wiley.
- Brand, B. L., & Alexander, P. C. (2003). Coping with incest: The relationship between recollections of childhood coping and adult functioning in female survivors of incest. Journal of Traumatic Stress: Official Publication of The International Society for Traumatic Stress Studies, 16(3), 285-293.
- Browning, D. H., & Boatman, B. (1977). Incest: Children at risk. The American Journal of Psychiatry.
- Butler, S. (1996). Conspiracy of silence: The trauma of incest. Volcano Press.
- Canavan, M. M., Meyer III, W. J., & Higgs, D. C. (1992). The female experience of sibling incest. Journal of Marital and Family Therapy, 18(2), 129-142.
- Carlson, B. E., Maciol, K., & Schneider, J. (2006). Sibling incest: Reports from forty-one survivors. Journal of child sexual abuse, 15(4), 19-34.
- Celbis, O., Altın, İ., Ayaz, N., Börk, T., & Karatoprak, S. (2020). Evaluation of incest cases: 4-years retrospective study. Journal of child sexual abuse, 29(1), 79-89.
- Choate, P., & Sharan, R. (2021). The Need to Act: Incest as a Crime Given Low Priority—A View with India as an Example. Social Sciences, 10(4), 142.
- Cohen, J. A., & Mannarino, A. P. (1991). Incest. Case studies in family violence, 171-186.
- Cole, P. M., & Putnam, F. W. (1992). Effect of incest on self and social functioning: A developmental psychopathology perspective. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 60(2), 174.
- Courtois, C. (1979). The incest experience and its aftermath. Victimology: An International Journal, 4(4), 337-347.
- Courtois, C. E. (1989). Healing the incest wound. New York: Guilford Press.
- Cyr, M., Wright, J., McDuff, P., & Perron, A. (2002). Intrafamilial sexual abuse: Brother–sister incest does not differ from father–daughter and stepfather–stepdaughter incest. Child Abuse & Neglect, 26(9), 957-973.
- DeMause, L. (1991). The universality of incest. The Journal of Psychohistory.
- Dietz, C. A., & Craft, J. L. (1980). Family dynamics of incest: A new perspective. Social Casework, 61(10), 602-609.
- Ellenson, G. S. (1985). Detecting a history of incest: A predictive syndrome. Social Casework, 66(9), 525-532.
- Erickson, M. T. (1993). Rethinking Oedipus: an evolutionary perspective of incest avoidance. The American journal of psychiatry.
- Everson, M. D., Hunter, W. M., Runyon, D. K., Edelsohn, G. A., & Coulter, M. L. (1989). Maternal support following disclosure of incest. American journal of Orthopsychiatry, 59(2), 197-207.
- Felitti, V. J. (1991). Long-term medical consequences of incest, rape, and molestation. Southern medical journal, 84(3), 328-331.
- Fessler, D. M., & Navarrete, C. D. (2004). Third-party attitudes toward sibling incest: Evidence for Westermarck’s hypotheses. Evolution and Human Behavior, 25(5), 277-294.
- Fox, J. R. (1962). Sibling incest. The British Journal of Sociology, 13(2), 128-150.
- Freedman, S. R., & Enright, R. D. (1996). Forgiveness as an intervention goal with incest survivors. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 64(5), 983.
- Gelinas, D. J. (1983). The persisting negative effects of incest. Psychiatry, 46(4), 312-332.
- Gilgun, J. F. (1995). We shared something special: The moral discourse of incest perpetrators. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 265-281.
- Goodwin, J. (1982). Sexual abuse: Incest victims and their families. Littleton, MA: J. Wright.
- Goodwin, J., Cormier, L., & Owen, J. (1983). Grandfather-granddaughter incest: A trigenerational view. Child abuse & neglect, 7(2), 163-170.
- Goody, J. (1956). A comparative approach to incest and adultery. The British Journal of Sociology, 7(4), 286-305.
- Gqgabi, R. B., & Smit, E. I. (2019). Psycho-Social Effects of Father–Daughter Incest: Views of South African Social Workers. Journal of child sexual abuse, 28(7), 840-859.
- Green, S. P. (2019). Incest. The Palgrave Handbook of Applied Ethics and the Criminal Law, 337-357.
- Groth, A. N. (1982). The incest offender. Handbook of clinical intervention in child sexual abuse, 215-239.
- Gul, H., Gul, A., Yurumez, E., & Öncü, B. (2020). Voices of adolescent incest victims: A qualitative study on feelings about trauma and expectations of recovery. Archives of psychiatric nursing, 34(2), 67-74.
- Hamer, M. (2002). Incest: A new perspective. Blackwell Publishing.
- Harkins, G. (2009). Everybody’s family romance: Reading incest in neoliberal America. U of Minnesota Press.
- Henderson, D. J. (1972). Incest: A synthesis of data. Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal, 17(4), 299-313.
- Henderson, J. (1983). Is incest harmful?. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 28(1), 34-40.
- Herman, J. (1981). Father–daughter incest. Professional Psychology, 12(1), 76.
- Herman, J., & Hirschman, L. (1977). Father-daughter incest. Signs: Journal of women in culture and society, 2(4), 735-756.
- Herman, J., & Hirschman, L. (1984). Families at risk for father-daughter incest. The Gender Gap in Psychotherapy: Social Realities and Psychological Processes, 259-264.
- Herman, J., Russell, D., & Trocki, K. (1986). Long-term effects of incestuous abuse in childhood. The American Journal of Psychiatry.
- Hurley, D. L. (1991). Women, alcohol and incest: an analytical review. Journal of studies on alcohol, 52(3), 253-268.
- Jacobs, J. L. (1994). Victimized daughters: Incest and the development of the female self. Taylor & Frances/Routledge.
- Kluft, R. P. (1990). Incest-related syndromes of adult psychopathology (Vol. 140). American Psychiatric Pub.
- Koenig, W. D., & Haydock, J. O. S. E. P. H. (2004). Incest and incest avoidance. Ecology and evolution of cooperative breeding in birds, 142-156.
- Kuper, A. (2009). Incest and influence: The private life of bourgeois England. Harvard University Press.
- Laviola, M. (1992). Effects of older brother-younger sister incest: A study of the dynamics of 17 cases. Child Abuse & Neglect, 16(3), 409-421.
- Lawson, D. M., & Akay-Sullivan, S. (2020). Considerations of dissociation, betrayal trauma, and complex trauma in the treatment of incest. Journal of child sexual abuse, 29(6), 677-696.
- Lester, D. (1972). Incest. Journal of sex research, 8(4), 268-285.
- Lew, M. (1988). Victims no longer: Men recovering from incest and other sexual child abuse. Perennial Library.
- Lieberman, D., Tooby, J., & Cosmides, L. (2003). Does morality have a biological basis? An empirical test of the factors governing moral sentiments relating to incest. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 270(1517), 819-826.
- Lindberg, F. H., & Distad, L. J. (1985). Post-traumatic stress disorders in women who experienced childhood incest. Child Abuse & Neglect, 9(3), 329-334.
- Lindzey, G. (1967). Some remarks concerning incest, the incest taboo, and psychoanalytic theory. American psychologist, 22(12), 1051.
- Lukianowicz, N. (1972). Incest: I: Paternal Incest. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 120(556), 301-313.
- Luo, L. (2011). Is there a sensitive period in human incest avoidance?. Evolutionary Psychology, 9(2), 147470491100900213.
- LUSTIG, C. N., DRESSER, C. J. W., SPELLMAN, M. S. W., & MURRAY, M. T. B. (1966). Incest: A family group survival pattern. Archives of General Psychiatry, 14(1), 31-40.
- Madonna, P. G., Van Scoyk, S., & Jones, D. P. (1991). Family interactions within incest and nonincest families. The American journal of psychiatry.
- Maltz, W., & Holman, B. (1987). Incest and sexuality. Lexington Bks..
- McCarty, L. M. (1986). Mother-child incest: Characteristics of the offender. Child welfare, 447-458.
- McDonnell, B. H. (2003). Is incest next. Cardozo Women’s LJ, 10, 337.
- Meiselman, K. C. (1978). Incest: A psychological study of causes and effects with treatment recommendations. Jossey-Bass.
- Mondragon, N. I., Munitis, A. E., & Txertudi, M. B. (2022). The breaking of secrecy: Analysis of the hashtag# MeTooInceste regarding testimonies of sexual incest abuse in childhood. Child Abuse & Neglect, 123, 105412.
- Myer, M. H. (2016). A new look at mothers of incest victims. In Feminist perspectives on social work and human sexuality (pp. 47-58). Routledge.
- Nakashima, I. I., & Zakus, G. E. (1977). Incest: Review and clinical experience. Pediatrics, 60(5), 696-701.
- Nasjleti, M. (1980). Suffering in silence: The male incest victim. Child Welfare, 269-275.
- Parsons, T. (1963). The incest taboo in relation to social structure and the socialization of the child.
- Pendergrast, M. (1995). Victims of memory: Incest accusations and shattered lives. Upper Access.
- Phelan, P. (1995). Incest and its meaning: The perspectives of fathers and daughters. Child abuse & neglect, 19(1), 7-24.
- Phillips-Green, M. J. (2002). Sibling incest. The Family Journal, 10(2), 195-202.
- Pribor, E. F., & Dinwiddie, S. H. (1992). Psychiatric correlates of incest in childhood. The American journal of psychiatry.
- Raphling, D. L., Carpenter, B. L., & Davis, A. (1967). Incest: A genealogical study. Archives of General Psychiatry, 16(4), 505-511.
- Riemer, S. (1940). A research note on incest. American Journal of Sociology, 45(4), 566-575.
- Rist, K. (1979). Incest: Theoretical and clinical views. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 49(4), 680.
- Roesler, T. A., & Wind, T. W. (1994). Telling the secret: Adult women describe their disclosures of incest. Journal of interpersonal Violence, 9(3), 327-338.
- Rudd, J. M., & Herzberger, S. D. (1999). Brother-sister incest—father-daughter incest: A comparison of characteristics and consequences. Child Abuse & Neglect, 23(9), 915-928.
- Russell, D. E. (1986). The secret trauma: Incest in the lives of girls and women, Rev. Basic Books.
- Sancak, B., Tasdemir, I., & Karamustafalioglu, O. (2021). Mother–daughter incest: A brief review of literature and case report. Journal of forensic sciences, 66(5), 2054-2059.
- Sariola, H., & Uutela, A. (1996). The prevalence and context of incest abuse in Finland. Child abuse & neglect, 20(9), 843-850.
- Schaich Borg, J., Lieberman, D., & Kiehl, K. A. (2008). Infection, incest, and iniquity: Investigating the neural correlates of disgust and morality. Journal of cognitive neuroscience, 20(9), 1529-1546.
- Schneider, D. M. (1976). The meaning of incest. The Journal of the Polynesian Society, 85(2), 149-169.
- Seehuus, M., Clifton, J., Khodakhah, D., & Lander, M. (2022). The Study of Sexual Fantasy in Women: a Review of the Findings and Methodological Challenges. Current Sexual Health Reports, 1-9.
- Seto, M. C., Lalumiere, M. L., & Kuban, M. (1999). The sexual preferences of incest offenders. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 108(2), 267.
- Simon, B. (1992). “Incest—see under oedipus complex”: The history of an error in psychoanalysis. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 40(4), 955-988.
- Sloane, P., & Karpinski, E. (1942). Effects of incest on the participants. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 12(4), 666.
- Smith, H., & Israel, E. (1987). Sibling incest: A study of the dynamics of 25 cases. Child Abuse & Neglect, 11(1), 101-108.
- Thorslev, P. L. (1965). Incest as Romantic Symbol. Comparative Literature Studies, 2(1), 41-58.
- Tidefors, I., Arvidsson, H., Ingevaldson, S., & Larsson, M. (2010). Sibling incest: A literature review and a clinical study. Journal of sexual aggression, 16(3), 347-360.
- Turner, J. H., & Maryanski, A. (2015). Incest: Origins of the taboo. Routledge.
- Van den Berghe, P. L. (1980). Incest and exogamy: A sociobiological reconsideration. Ethology and Sociobiology, 1(2), 151-162.
- Wagner, R. (1972). Incest and identity: a critique and theory on the subject of exogamy and incest prohibition. Man, 7(4), 601-613.
- Weinberg, S. K. (1955). Incest behavior.
- Weiner, I. B. (1964). On incest: A survey. Excerpta Criminologica, 4, 137-155.
- Wescott, S., & Kosmala, K. (2022). Current perspectives on pornography use by individuals convicted of a sexual offense. Current psychiatry reports, 24(11), 671-678.
- Westerlund, E. (1992). Women’s sexuality after childhood incest. WW Norton & Co.
- Wolf, A. P. (1966). Childhood Association, Sexual Attraction, and the Incest Taboo: A Chinese Case 1. American Anthropologist, 68(4), 883-898.
- Wolf, A. P. (2005). Inbreeding, incest, and the incest taboo: The state of knowledge at the turn of the century.
- Yates, A. (1982). Children eroticized by incest. The American Journal of Psychiatry.
